Installing the G-ADOPT library
First of all, you need to install Firedrake, the finite element framework underpinning G-ADOPT. Firedrake is available for Ubuntu, Mac, and, in principle, other Linux and Linux-like systems.
Up to date, detailed instructions for installing Firedrake and suggestions for troubleshooting can be found on the Installing Firedrake page of the Firedrake website.
Installing G-ADOPT
With Firedrake installed, you can install the G-ADOPT library:
source venv-firedrake/bin/activate
python3 -m pip install gadopt
This is only the base installation of G-ADOPT. You can install extra dependencies to run the tutorials or for nonlinear optimisation.
Using the G-ADOPT library
If you would like to run G-ADOPT through scripts or interactively, simply ensure that your Firedrake environment is activated:
source venv-firedrake/bin/activate
Furthermore, the gadopt Python module should be available for you to use.
Run the tutorials
The G-ADOPT tutorials are located within the G-ADOPT GitHub repository. If you would like to experiment with them, there are a few more requirements for your Firedrake environment.
First, activate the Firedrake environment so that the requirements will be installed into it:
source venv-firedrake/bin/activate
Next, install Jupyter Notebook and the optional G-ADOPT requirements:
python3 -m pip install notebook gadopt[demos,optimisation] pygplates
Finally, clone the G-ADOPT repository to access the demos:
git clone https://github.com/g-adopt/g-adopt
Now you should be ready to test the installation and run the first tutorial! Start the notebook server:
jupyter notebook
Within the browser window that pops up, you can browse to the
g-adopt/demos directory and open any Python script with the .py
extension as a notebook.
The tutorials can also be run in the JupyterLab environment on the ARE after following the instructions below.
Visualisation software
Firedrake can output data in VTK format, suitable for viewing in Paraview. On Ubuntu and similar systems, you can obtain Paraview by installing the paraview package. On Mac OS the easiest approach is to download a binary from the paraview website.
Optional install
To bring in the optional nonlinear optimisation dependencies you should activate the virtual environment of an existing Firedrake installation and then install the optimisation variant:
pip install gadopt[optimisation]
Using the G-ADOPT library on Gadi
For existing users of NCI's Gadi HPC system, the G-ADOPT team
maintains an up-to-date G-ADOPT and Firedrake installation with all
optional dependencies. This requires that you already have an NCI
account and are a member of an existing project with some compute
allocation. To gain access to G-ADOPT on Gadi, follow this
link to request to
join the fp50 project. This is a small project intended only for
providing access to G-ADOPT, and must not be used as a PBS project
(except for requesting storage access, as below).
Once your request is approved, you can access G-ADOPT on Gadi by running:
module use /g/data/fp50/modules
module load g-adopt
To use G-ADOPT in your batch scripts, you'll need to add the following to your PBS flags:
-lstorage=gdata/fp50
By default, this will give you the latest release of G-ADOPT, and load the
most recent firedrake module. If you wish to use your own G-ADOPT installation, set
the environment variable MY_GADOPT and load the firedrake module.
export MY_GADOPT=/g/data/ab12/path/to/my/gadopt
module use /g/data/fp50/modules
module load firedrake
You can also use G-ADOPT in a JupyterLab session on the
ARE at
NCI. When launching a JupyterLab session, add gdata/fp50 to the storage
field and the following in the 'Advanced options' section:
To run the demos on the ARE, untar the demos.tgz file found in /g/data/fp50/apps/firedrake/gadopt
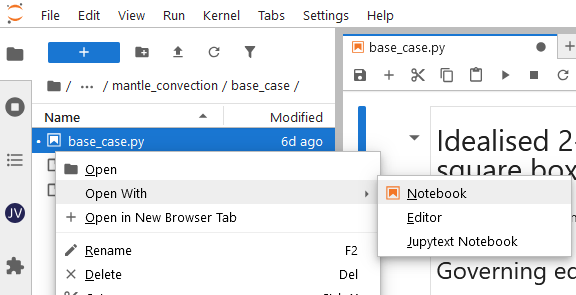
into your /scratch directory. Once the ARE session has started, navigate to one of the demo
directories, right click on the .py file and select Open With -> Notebook
The demos can also be run in parallel on the standard job queues. For example, the following
script, when placed in the mantle_convection/3d_spherical directory will run that demo on 4
cores in Gadi's 'normal' queue:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
#PBS -P [YOUR_PROJECT]
#PBS -lncpus=4
#PBS -lmem=16GB
#PBS -lwalltime=00:15:00
#PBS -lstorage=scratch/[YOUR_PROJECT]+gdata/fp50
#PBS -ljobfs=10GB
#PBS -lwd
#PBS -qnormal
module use /g/data/fp50/modules
module load g-adopt
mpiexec python3 3d_spherical.py
Developing G-ADOPT
If you are keen to make changes to the core G-ADOPT code (and you want to work in a separate directory to Firedrake's default location for G-ADOPT), you should first clone the G-ADOPT GitHub repository:
git clone https://github.com/g-adopt/g-adopt.git
After activating the virtual environment of an existing Firedrake installation, you can then install G-ADOPT with:
pip install -e g-adopt/
The editable, -e, flag means that any updates you make to this directory will be reflected directly in the Firedrake virtual environment.